Who Invented The Light Bulb: A Fascinating Journey Through Time
Let’s talk about one of the most revolutionary inventions in human history—the light bulb. Imagine life without it. No reading under a cozy lamp, no streetlights guiding you home, and definitely no neon signs flashing in Times Square. The light bulb transformed our world, turning darkness into light with just a flick of a switch. But who exactly invented this game-changing device? Let’s dive in and uncover the story behind the person—or people—who brought illumination to our lives.
Now, you might think it’s all about Thomas Edison, right? Well, hold your horses. Edison’s name is definitely tied to the light bulb, but he wasn’t the only player in this invention saga. The creation of the light bulb was a collaborative effort spanning decades, with contributions from inventors all over the globe. So, buckle up as we explore the twists and turns of this incredible journey.
This story isn’t just about who came up with the idea first. It’s about innovation, perseverance, and how a simple idea evolved into one of the most impactful inventions in history. By the end of this article, you’ll have a newfound appreciation for the light bulb and the brilliant minds behind it. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- Early Experiments: The First Sparks of Light
- Thomas Edison: The Man Behind the Myth
- Other Contributors: The Forgotten Inventors
- Innovation Over Time: How the Light Bulb Evolved
- Impact on Society: How Light Changed the World
- Modern-Day Advancements: The Future of Lighting
- Biography: Thomas Edison, the Wizard of Menlo Park
- Common Misconceptions About the Light Bulb
- Environmental Considerations: The Green Side of Lighting
- Final Thoughts: Celebrating the Legacy of the Light Bulb
Early Experiments: The First Sparks of Light
Before we talk about Edison and his famous bulb, let’s rewind to the early days of electric lighting. The quest to harness electricity for illumination began long before Edison entered the scene. Back in the early 1800s, inventors were already tinkering with electric arcs and incandescent filaments. These were the first baby steps toward the modern light bulb.
One of the earliest pioneers was Humphry Davy, an English chemist who demonstrated the first electric arc lamp in 1802. He used a high-voltage battery to create a blinding arc of light between two carbon rods. While it wasn’t practical for everyday use, it proved that electricity could produce light. This was a big deal at the time, and it sparked (pun intended) a wave of innovation.
Throughout the 19th century, dozens of inventors tried to improve on Davy’s work. Warren De La Rue, a British scientist, experimented with platinum filaments in the 1840s. Joseph Swan, another British inventor, developed a carbonized paper filament in the 1860s. These early attempts faced challenges like high costs, short lifespans, and inefficiency, but they laid the groundwork for what was to come.
Why Was This Important?
- These early experiments showed that electric lighting was possible, even if it wasn’t yet practical.
- They paved the way for future inventors to refine the technology.
- The race to create a commercially viable light bulb was officially on.
Thomas Edison: The Man Behind the Myth
Okay, let’s talk about the big guy—Thomas Edison. Born in 1847 in Milan, Ohio, Edison was a self-taught inventor with a knack for turning ideas into reality. By the time he tackled the light bulb, he already had dozens of patents under his belt. But the light bulb wasn’t just another invention for Edison—it was his magnum opus.
Edison’s approach was methodical and relentless. He tested thousands of materials to find the perfect filament that would glow brightly without burning out quickly. After years of trial and error, he finally succeeded in 1879 by using a carbonized bamboo filament. This breakthrough made his light bulb practical, affordable, and long-lasting—exactly what the world needed.
But Edison didn’t stop there. He also developed an entire electrical system to power his bulbs, including generators, wires, and switches. This holistic approach ensured that his invention wasn’t just a standalone product but part of a larger ecosystem that could transform homes and cities.
Why Did Edison Succeed?
- He had a team of skilled researchers at Menlo Park, his famous lab.
- He focused on both the technology and the infrastructure needed to support it.
- His business acumen helped him commercialize his invention on a massive scale.
Other Contributors: The Forgotten Inventors
While Edison gets most of the credit, he wasn’t the only one working on the light bulb. In fact, several inventors made significant contributions that are often overlooked. Let’s give them their due.
Joseph Swan, for example, developed a working incandescent bulb in England around the same time as Edison. His design used a carbonized paper filament and was even demonstrated publicly in 1878. Swan eventually formed a partnership with Edison, leading to the creation of the Edison and Swan United Electric Light Company.
Another key figure was Lewis Latimer, an African American inventor who worked with Edison. Latimer improved the bulb’s filament by inventing a process to produce carbon filaments more efficiently. His innovations helped make the light bulb more durable and cost-effective.
There were also inventors like Heinrich Göbel in Germany and William Sawyer and Albon Man in the U.S., who all contributed to the development of electric lighting. These unsung heroes remind us that invention is rarely a solo effort.
Why Recognize These Contributors?
- They remind us that innovation is a collaborative process.
- They highlight the global nature of scientific progress.
- They give credit where credit is due, ensuring history is told accurately.
Innovation Over Time: How the Light Bulb Evolved
The light bulb didn’t stop evolving after Edison’s breakthrough. Over the years, inventors and engineers continued to improve on the original design, making it more efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly.
In the early 20th century, tungsten filaments replaced carbon filaments, increasing the bulb’s brightness and lifespan. Then came the invention of the halogen bulb in the 1950s, which used halogen gas to prevent the filament from deteriorating. These advancements made electric lighting even more practical for everyday use.
Fast forward to today, and we have LED (light-emitting diode) technology, which is revolutionizing the lighting industry. LEDs are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and versatile, making them the go-to choice for modern lighting solutions. They’re used everywhere from homes to stadiums to smartphones.
What Does This Mean for the Future?
- Lighting technology will continue to evolve, driven by the need for sustainability and efficiency.
- Smart lighting systems will become more common, allowing users to control their lights with apps and voice commands.
- The focus will shift toward creating lighting solutions that benefit both people and the planet.
Impact on Society: How Light Changed the World
The invention of the light bulb didn’t just brighten our homes—it transformed society in countless ways. It extended the productive hours of the day, allowing people to work, study, and socialize long after sunset. It also enabled the growth of industries like manufacturing, entertainment, and transportation.
Cities became safer and more vibrant with the installation of streetlights. Factories could operate 24/7, boosting productivity and economic growth. And let’s not forget the cultural impact—think about movie theaters, concert halls, and sports arenas, all made possible by electric lighting.
But the light bulb’s influence goes beyond practical applications. It symbolizes human ingenuity and our ability to overcome challenges. It’s a reminder that even the darkest nights can be illuminated with the right ideas and effort.
Modern-Day Advancements: The Future of Lighting
Today, lighting technology is at the forefront of the green energy movement. LED bulbs, smart lighting systems, and solar-powered solutions are paving the way for a more sustainable future. These innovations not only save energy but also reduce our carbon footprint, making them essential for combating climate change.
Smart lighting systems, powered by IoT (Internet of Things) technology, are becoming increasingly popular. These systems allow users to customize their lighting based on mood, time of day, and even weather conditions. Imagine walking into a room and having the lights adjust automatically to your preferences—cool, huh?
Looking ahead, we can expect even more breakthroughs in lighting technology. From bioluminescent materials to wireless power transmission, the possibilities are endless. The light bulb’s legacy will continue to inspire generations of inventors and innovators.
Biography: Thomas Edison, the Wizard of Menlo Park
Let’s take a closer look at the man who changed the world with his light bulb. Thomas Alva Edison was born on February 11, 1847, in Milan, Ohio. From a young age, he showed a keen interest in science and technology. Despite having little formal education, he taught himself through reading and experimentation.
Edison’s career as an inventor began in the 1860s when he worked as a telegraph operator. This experience gave him a deep understanding of electricity, which he later applied to his inventions. Over his lifetime, he earned over 1,000 patents for inventions ranging from the phonograph to the motion picture camera.
Here’s a quick rundown of Edison’s life:
| Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Thomas Alva Edison |
| Birth Date | February 11, 1847 |
| Birthplace | Milan, Ohio |
| Occupation | Inventor, Entrepreneur |
| Notable Inventions | Light Bulb, Phonograph, Motion Picture Camera |
| Death Date | October 18, 1931 |
Common Misconceptions About the Light Bulb
There are a few myths surrounding the invention of the light bulb that need to be addressed. First, let’s clear up the idea that Edison was the sole inventor. As we’ve seen, many inventors contributed to the development of electric lighting. Edison’s genius lay in his ability to refine and commercialize the technology.
Another misconception is that the light bulb was an overnight success. In reality, it took years of experimentation and refinement before it became practical for everyday use. Edison and his team faced countless setbacks and failures before achieving their breakthrough.
Finally, some people think that the light bulb was the first form of electric lighting. As we discussed earlier, electric arcs and other forms of lighting existed long before Edison’s bulb. What set his invention apart was its affordability, durability, and ease of use.
Environmental Considerations: The Green Side of Lighting
In today’s world, sustainability is a top priority. That’s why modern lighting solutions focus on reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact. LED bulbs, for example, use up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer.
Solar-powered lighting is another promising development. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems provide clean, renewable energy for homes and communities. They’re especially beneficial in areas without access to traditional power grids.
As we move forward, it’s crucial to balance innovation with environmental responsibility. The light bulb’s legacy can inspire us to create technologies that not only improve our lives but also protect our

Qui a invente l'ampoule ? Quiainvente.eu

Qui a vraiment inventé l'ampoule
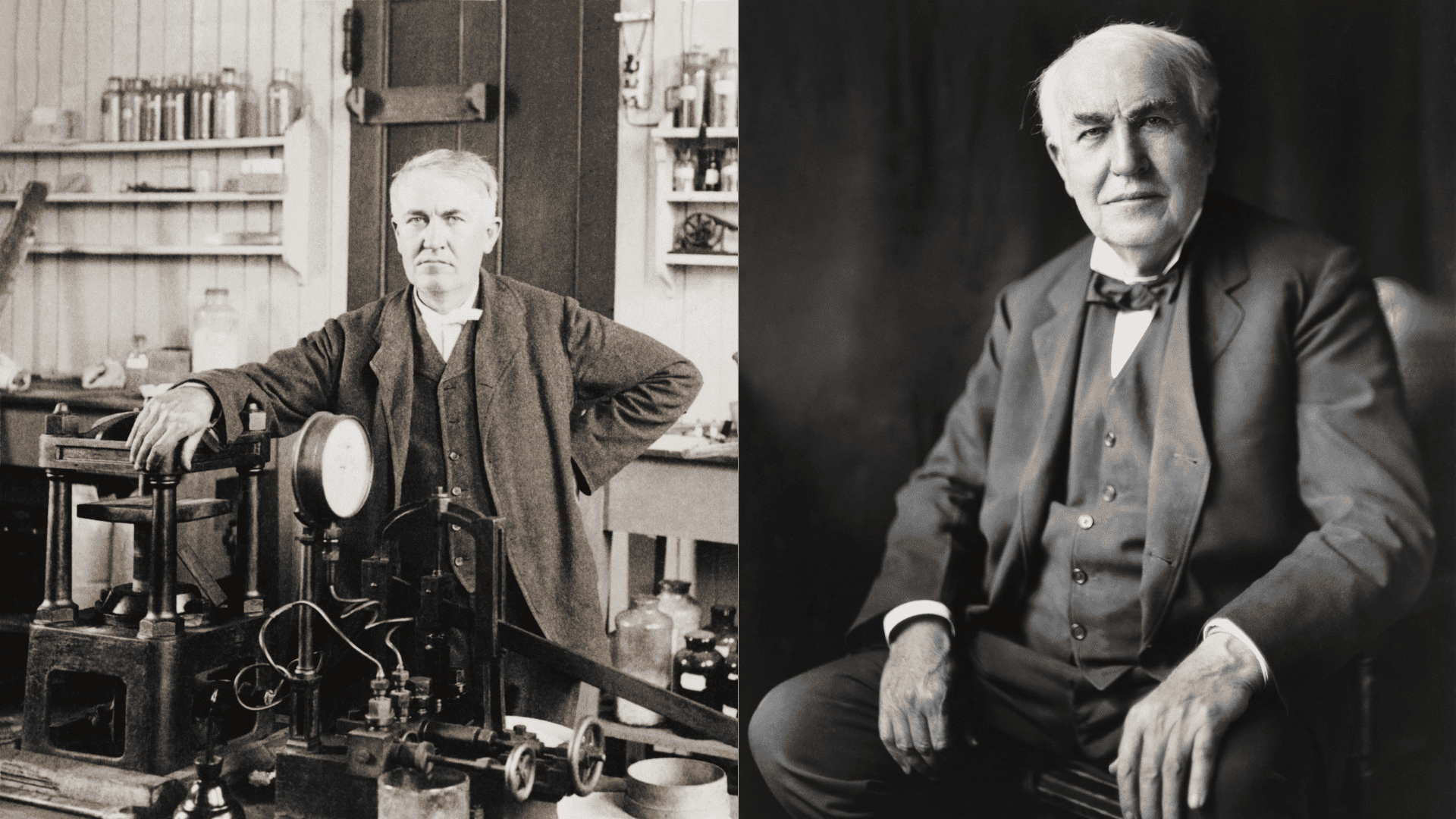
Découvrez Enfin Qui A Inventé l'Ampoule Lustria