Explosive And Effusive Volcanoes: A Deep Dive Into Their Mysteries
Ever wondered what makes some volcanoes explode like fireworks while others ooze lava like molten honey? Well, buckle up because we’re about to take a wild ride into the world of explosive and effusive volcanoes. These geological wonders aren’t just random eruptions; they’re the result of complex processes that have shaped our planet for millions of years. So, let’s break it down and uncover the secrets behind these fiery giants.
Volcanoes are nature’s way of reminding us who’s boss. Whether they’re spitting out ash clouds that block out the sun or slowly building new land with rivers of molten rock, they’re forces to be reckoned with. And guess what? Not all volcanoes are created equal. Some go boom, and others go sloooow. Understanding the difference between explosive and effusive volcanoes can save lives, shape landscapes, and even influence global climate patterns.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the science, history, and impact of these volcanic phenomena. From the deadliest eruptions in history to the quiet oozing of basaltic lava, we’ve got you covered. So, grab your hiking boots and let’s explore the fiery underworld together!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Volcanic Activity
- What Makes a Volcano Explosive?
- The Calm Before the Flow: Effusive Volcanoes
- Explosive vs Effusive: Key Differences
- The Science Behind It All
- Historic Eruptions That Shaped Our World
- How Volcanoes Impact the Planet
- Staying Safe Around Volcanoes
- Predicting the Next Big Eruption
- Wrapping It Up
Introduction to Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is like Earth’s version of a pressure cooker. Beneath the surface, molten rock, gases, and other materials are constantly moving around, waiting for an opportunity to escape. When they do, it can be either explosive or effusive, depending on a bunch of factors. Let’s start with the basics.
What Causes Volcanoes?
Volcanoes are born from the movement of tectonic plates. When these massive slabs of Earth’s crust collide, pull apart, or slide past each other, magma from the mantle can rise to the surface. This magma can have different compositions, which determine whether the eruption will be explosive or effusive. It’s kind of like how different ingredients in a recipe can change the taste of your meal.
What Makes a Volcano Explosive?
Explosive volcanoes are the rockstars of the geological world. They make headlines, destroy cities, and inspire awe in equal measure. But what exactly makes them so explosive? The answer lies in the chemistry of the magma.
- Hikaru Nagi A Rising Star In Japanese Entertainment
- Watch Filmyfly 2025 Bollywood South Hindi Movies Online
High Viscosity and Gas Content
Explosive eruptions happen when magma is thick and sticky, or what scientists call high viscosity. This happens because the magma is rich in silica, which makes it resistant to flow. As if that wasn’t enough, this type of magma also contains a lot of dissolved gases. When the pressure builds up, it’s like shaking a soda can and then popping the top – kaboom!
Famous Explosive Volcanoes
- Mount St. Helens (USA)
- Krakatoa (Indonesia)
- Mount Vesuvius (Italy)
These volcanoes have left their mark on history, sometimes literally. The ash from Krakatoa’s 1883 eruption circled the globe, causing colorful sunsets for years. Meanwhile, Mount Vesuvius famously buried Pompeii under a layer of ash and pumice, preserving the city like a time capsule.
The Calm Before the Flow: Effusive Volcanoes
On the other end of the spectrum, we have effusive volcanoes. These guys are more like the chill cousins of their explosive relatives. Instead of blowing their tops, they prefer to ooze lava in a slow and steady manner.
Low Viscosity Magma
Effusive eruptions occur when magma is low in silica and rich in iron and magnesium. This makes it runny and easy to flow, like honey on a warm day. Basaltic magma is the most common type associated with effusive eruptions, and it often creates shield volcanoes – broad, gently sloping mountains that look like shields lying on the ground.
Examples of Effusive Volcanoes
- Kilauea (Hawaii)
- Erebus (Antarctica)
- Erta Ale (Ethiopia)
Kilauea in Hawaii is one of the most active volcanoes in the world, and its lava flows have added new land to the island over the years. Erebus, on the other hand, is famous for its lava lake, which is one of the few permanent ones on Earth.
Explosive vs Effusive: Key Differences
Now that we’ve looked at both types of volcanoes, let’s compare them side by side. Understanding the differences can help us predict eruptions and prepare for their impacts.
Key Factors
- Magma Composition: Explosive volcanoes have high-silica magma, while effusive volcanoes have low-silica magma.
- Gas Content: Explosive eruptions are driven by high gas pressure, whereas effusive eruptions have lower gas content.
- Eruption Style: Explosive volcanoes produce ash, pyroclastic flows, and towering eruption columns, while effusive volcanoes produce lava flows.
It’s like comparing a fireworks display to a slow-moving river. Both are impressive in their own ways, but they have very different effects on the environment.
The Science Behind It All
Behind every volcanic eruption lies a complex interplay of physics, chemistry, and geology. Let’s break it down.
The Role of Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is the driving force behind most volcanic activity. When plates collide, subduct, or rift apart, magma finds its way to the surface. The type of plate boundary influences the kind of magma that forms, which in turn determines whether the eruption will be explosive or effusive.
How Magma Chemistry Matters
Magma composition plays a huge role in eruption style. Silica-rich magma is more viscous and traps gases, leading to explosive eruptions. On the flip side, silica-poor magma is less viscous and allows gases to escape easily, resulting in effusive eruptions.
Historic Eruptions That Shaped Our World
Volcanoes have played a major role in shaping human history and the planet itself. Some eruptions were so massive that they changed the course of civilizations.
The 1815 Eruption of Tambora
This Indonesian volcano caused what became known as the “Year Without a Summer.” The massive amount of ash and sulfur dioxide it spewed into the atmosphere blocked sunlight, leading to crop failures and famine worldwide.
The 1980 Eruption of Mount St. Helens
One of the most studied eruptions in modern history, Mount St. Helens blew its top in a lateral blast that flattened forests and killed 57 people. It provided scientists with valuable insights into explosive eruptions.
How Volcanoes Impact the Planet
Volcanoes don’t just affect the areas around them; they have global implications. From climate change to land formation, their impact is far-reaching.
Climate Effects
Large explosive eruptions can inject massive amounts of sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere, where it forms aerosols that reflect sunlight and cool the planet. This temporary cooling effect can last for years, influencing weather patterns worldwide.
Land Formation
Effusive volcanoes, especially those in Hawaii and Iceland, are responsible for creating new land. Over time, lava flows build up to form islands and expand coastlines, shaping the geography of our planet.
Staying Safe Around Volcanoes
Living near a volcano can be risky business, but with the right precautions, people can coexist with these natural wonders.
Monitoring and Early Warning Systems
Volcanologists use a variety of tools to monitor volcanic activity, including seismic sensors, gas emissions, and ground deformation. These systems provide early warnings that can save lives during an eruption.
Evacuation Plans
Communities near active volcanoes need well-thought-out evacuation plans. Regular drills and clear communication channels ensure that everyone knows what to do when an eruption is imminent.
Predicting the Next Big Eruption
While we can’t predict volcanic eruptions with absolute certainty, advances in technology are making it easier to forecast them. Satellites, drones, and computer models are all part of the arsenal used by scientists to monitor volcanoes.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning algorithms are being trained to recognize patterns in volcanic activity that might indicate an impending eruption. While still in its infancy, this technology holds promise for improving prediction accuracy.
Wrapping It Up
Volcanoes, whether explosive or effusive, are awe-inspiring reminders of Earth’s power. From shaping landscapes to influencing climate, they play a crucial role in the planet’s dynamics. Understanding the differences between these two types of eruptions helps us better prepare for their impacts and appreciate their beauty.
So, the next time you hear about a volcanic eruption in the news, take a moment to think about the incredible processes that made it happen. And if you’re ever lucky enough to witness one in person, remember to respect its power – and maybe bring a camera!
Got any questions or thoughts about volcanoes? Drop a comment below, and let’s keep the conversation going. Also, don’t forget to share this article with your friends who love geology as much as you do!
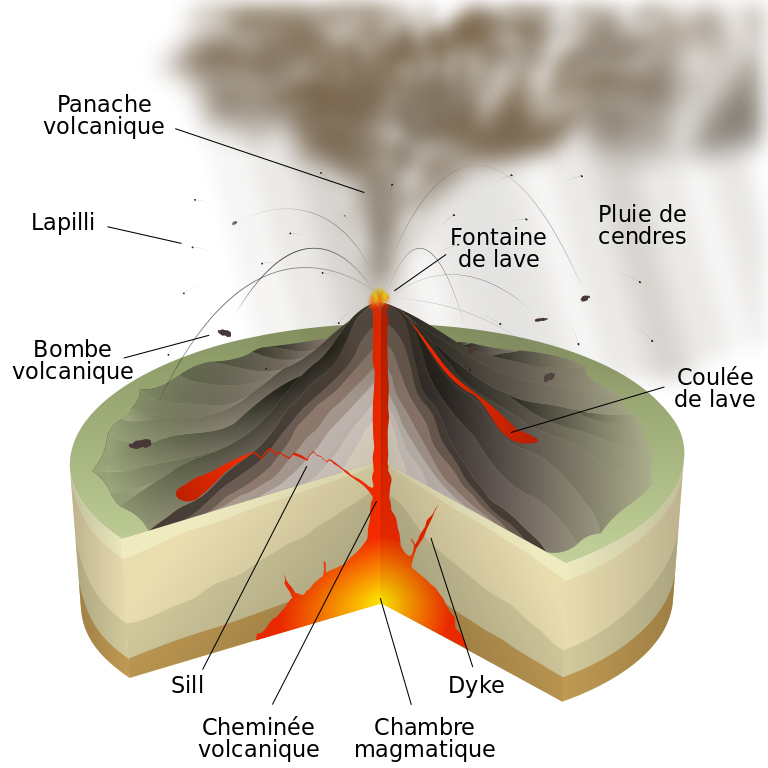
Schéma d’un volcan en éruption ScienceJunior.fr

Les Volcans Effusifs vrogue.co
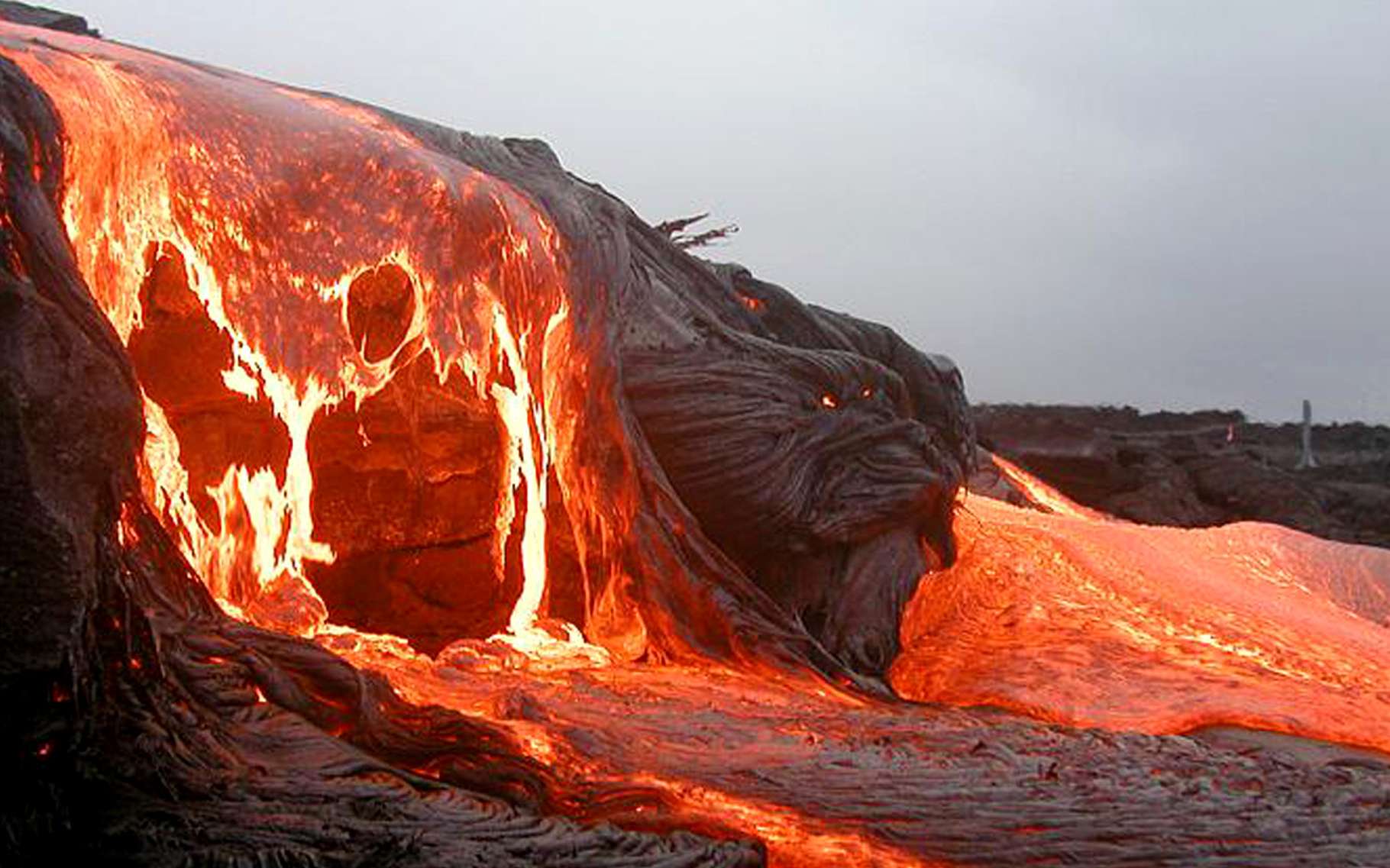

Les Volcans Effusifs vrogue.co